_id
683a1608c782e11e38d1b149
id
3164
title
Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS)
full_title
Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS)
short_title
ASPECTS
med_description
Determines MCA stroke severity using available CT data.
short_description
MCA stroke severity using CT data.
slug
alberta-stroke-program-early-ct-score-aspects
description
The Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) determines Middle Cerebral Arterial (MCA) stroke severity using available computed tomography data.
keywords
aspect score, aspect, early stroke, stroke, cva, id cva, id stroke early, stoke severity using CT, stroke severity CT, stroke prognosis
complaint
[ "Dizziness", "Headache", "Weakness" ]
formula
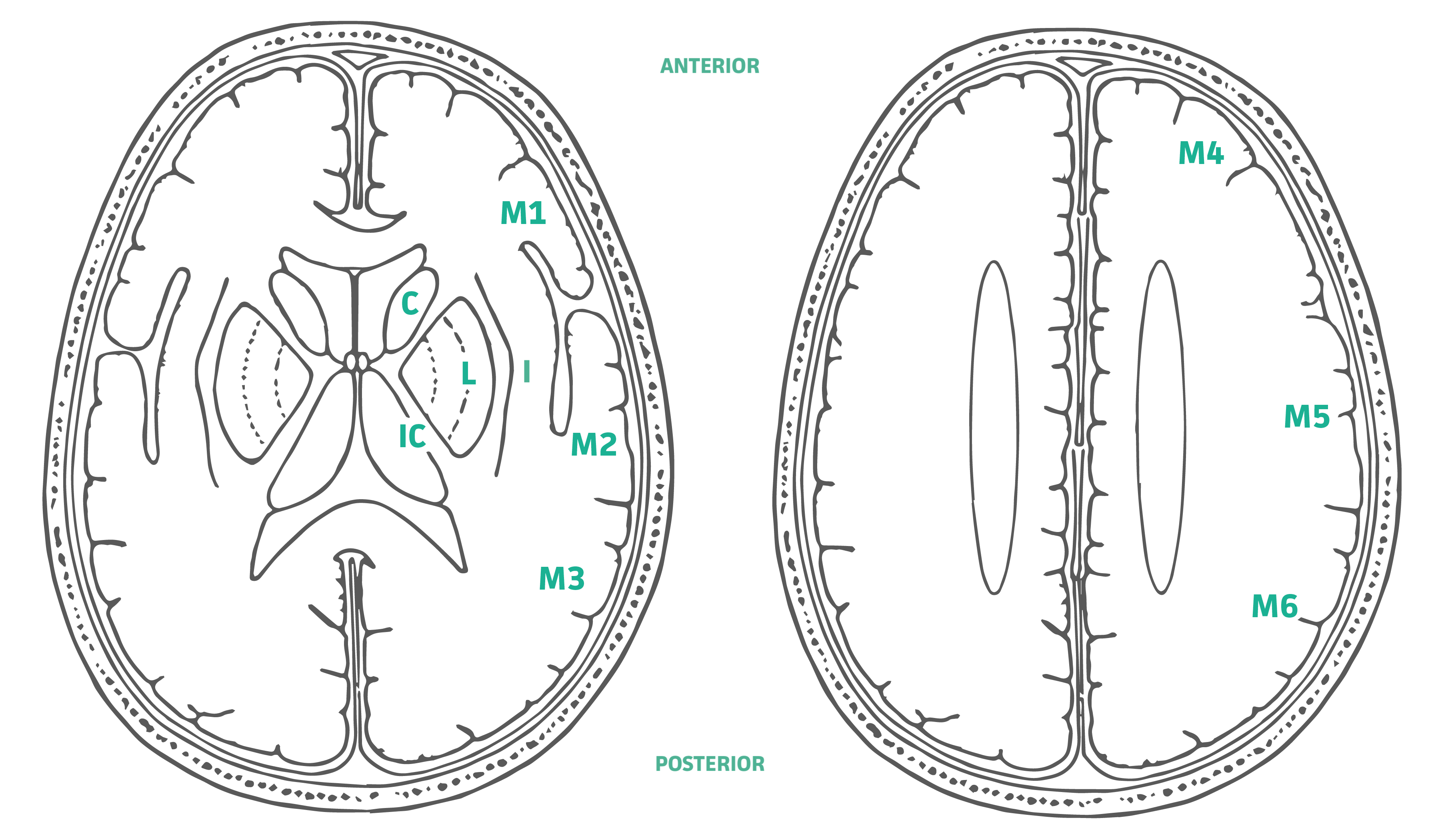
To compute the ASPECTS, 1 point is subtracted from 10 for any evidence of early ischemic change for each of the defined regions. A normal CT scan receives an ASPECTS of 10 points. An ASPECTS of ≤7 points highly correlates with negative functional outcome, determined byModified Rankin Scale (mRS). An ASPECTS of 0 indicates diffuse involvement throughout the MCA territory. Subcortical structures are allotted 3 points (C, L, and IC). MCA cortex is allotted 7 points (insular cortex, M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, and M6). Regions: C - Caudate IC - Internal Capsule L - Lentiform nucleus I - Insular ribbon M1 - Anterior MCA cortex M2 - MCA cortex lateral to the insular ribbon M3 - Posterior MCA cortex M4* M5* M6* *Anterior, lateral and posterior MCA territories immediately superior to M1, M2 and M3, rostral to basal ganglia.
evidence
There appears to be a lack of consistency in studies evaluating the interrater reliability of ASPECTS.
One 2018 trial comparing the evaluation of 43 patients using ASPECTS among senior radiology residents, a neuroradiology fellow and two senior neuroradiologists found agreement varied from 0.486 to 0.678 in Cohen's κ comparing the fellow to the neuroradiology staff, and 0.198 to 0.491 when compared to the senior radiology resident (Kobkitsuksakul 2018).
Using the binary outcome, a 2003 study of 34 cases found only 42% agreement for ASPECTS, with a kappa of 0.34 (Mak 2003).
In contrast, a 2014 trial of 214 patients using the binary outcome for patients in real time and then later by an expert assessor to be substantial, with a weighted kappa of 0.69 (Coutts 2004).
measurements
[]
information
- The ASPECTS is determined from evaluation of two standardized regions of the MCA territory: the basal ganglia level, where the thalamus, basal ganglia, and caudate are visible, and the supraganglionic level, which includes the corona radiata and centrum semiovale.
- All cuts with basal ganglionic or supraganglionic structures visible are required to determine if an area is involved. The abnormality should be visible on at least two consecutive cuts to ensure that it is truly abnormal rather than a volume averaging effect.
refrences
{ "Clinical Practice Guidelines": [], "Manufacturer Website": [], "Original/Primary Reference": [ { "href": "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10905241", "text": "Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Zhang J et-al. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. ASPECTS Study Group. Alberta Stroke Programme Early CT Score. Lancet. 2000;355 (9216): 1670-4." } ], "Other References": [ { "href": "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17921237", "text": "Aviv RI, Mandelcorn J, Chakraborty S et-al. Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Scoring of CT perfusion in early stroke visualization and assessment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28 (10): 1975-80." }, { "href": "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19765124", "text": "Puetz V, Dzialowski I, Hill MD et-al. The Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score in clinical practice: what have we learned?. Int J Stroke. 2009;4 (5): 354-64." }, { "href": "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24503670", "text": "Yoo AJ, Zaidat OO, Chaudhry ZA, et al. Impact of pretreatment noncontrast CT Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score on clinical outcome after intra-arterial stroke therapy. Stroke. 2014;45(3):746-51." }, { "href": "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29467112", "text": "Kobkitsuksakul C, Tritanon O, Suraratdecha V. Interobserver agreement between senior radiology resident, neuroradiology fellow, and experienced neuroradiologist in the rating of Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score (ASPECTS). Diagn Interv Radiol. 2018;24(2):104-107." }, { "href": "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12690213", "text": "Mak HK, Yau KK, Khong PL, et al. Hypodensity of >1/3 middle cerebral artery territory versus Alberta Stroke Programme Early CT Score (ASPECTS): comparison of two methods of quantitative evaluation of early CT changes in hyperacute ischemic stroke in the community setting. Stroke. 2003;34(5):1194-6." }, { "href": "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15073381", "text": "Coutts SB, Demchuk AM, Barber PA, et al. Interobserver variation of ASPECTS in real time. Stroke. 2004;35(5):e103-5." }, { "href": "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28277460", "text": "Prakkamakul S, Yoo AJ. ASPECTS CT in Acute Ischemia: Review of Current Data. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;26(3):103-112.Prakkamakul S, Yoo AJ. ASPECTS CT in Acute Ischemia: Review of Current Data. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;26(3):103-112." } ], "Outcomes": [], "Validation": [ { "href": "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11559501", "text": "Pexman JH, Barber PA, Hill MD et-al. Use of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) for assessing CT scans in patients with acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22 (8): 1534-42." } ], "Validations": [] }
pearls
- Quantifies CT changes in early middle cerebral artery stroke. More early changes seen on CT suggest poorer outcome from stroke.
- Patients with scores ≥8 have a better chance for an independent outcome.
Points to keep in mind:
- The score does not consistently predict treatment response or intracranial hemorrhage or offer nuanced prognostic information.
- ASPECTS has mainly been studied in patients treated with or eligible for stroke reperfusion therapy (tPA), which many stroke patients do not qualify for.
usecase
Patients presenting in the first minutes and hours of a stroke with clinical suspicion for middle cerebral artery occlusion.
reasons
Identifying patients with a greater likelihood of poor functional outcome (scores <8) may be helpful in the early stages of care for supporting transfer or therapy decisions.
next_advice
Using the traditional cutoff (<8 vs ≥8) as a rough estimate for predicting independence may help inform decisions. ASPECTS suggests that early CT changes in stroke may be a harbinger of poor outcomes.
More recent studies have evaluated ASPECTS on the basis of the entire scale, as well as dichotomous (<8 vs ≥8) or trichotomous (0-4, 5-7, and 8-10) divisions, but few robust prospective trials have been conducted (Prakkamakul 2017).
next_actions
The ASPECTS relies on subtle CT findings and thus requires an experienced radiologist. Its only validated use is as a binary variable (<8 vs ≥8) for general outcome prediction in those eligible for reperfusion therapy.
For patients being considered for intra-arterial tPA administration, ASPECTS may be useful to exclude patients not likely to do well in terms of functional independence (i.e., intra-arterial treatment likely to be futile) (Yoo 2014).
next_management
In patients presenting with symptoms concerning for ischemic stroke, the following are generally considered standard practice:
-
Neurology consultation.
-
Determine onset of stroke symptoms, or time patient last felt or was observed normal.
-
Stat head CT to rule out hemorrhagic stroke.
-
In appropriate circumstances and in consultation with both neurology and the patient, consider IV thrombolysis for ischemic strokes in patients with no contraindications.
-
Always consider stroke mimics in the differential diagnosis, especially in cases with atypical features (age, risk factors, history, physical exam), including:
-
Recrudescence of old stroke from metabolic or infectious stress.
-
Todd’s paralysis after seizure.
-
Complex migraine.
-
Pseudoseizure or conversion disorder.
diseases
[ "Stroke/TIA" ]
input_schema
{ "md_calc_info_concept": null, "option_fhir_rules": null, "type": "visual", "visual": "<p><img style=\"max-width: 100%;\" src=\"https://cdn-web-img.mdcalc.com/content/aspects2.png\" alt=\"\"></p>" }
{ "inct": null, "option_fhir_rules": null, "subheading": "Subcortical Structures", "subheading_instructions": "", "type": "subheading" }
{ "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Caudate (C)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "C", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }
{ "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Internal Capsule (IC)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "IC", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }
{ "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Lentiform nucleus (L)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "L", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }
{ "inct": null, "option_fhir_rules": null, "subheading": "MCA Cortex", "subheading_instructions": "", "type": "subheading" }
{ "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Insular Ribbon (I)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "I", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }
{ "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Anterior MCA cortex (M1)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M1", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }
{ "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "MCA cortex lateral to the insular ribbon (M2)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M2", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }
{ "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Posterior MCA cortex (M3)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M3", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }
{ "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "<p>Anterior cortex immediately rostral to M1 (M4)</p>", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M4", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }
{ "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "<p>Lateral cortex immediately rostral to M3 (M5)</p>", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M5", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }
{ "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "<p>Posterior cortex immediately rostral to M3 (M6)</p>", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M6", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }
[ { "md_calc_info_concept": null, "option_fhir_rules": null, "type": "visual", "visual": "<p><img style=\"max-width: 100%;\" src=\"https://cdn-web-img.mdcalc.com/content/aspects2.png\" alt=\"\"></p>" }, { "inct": null, "option_fhir_rules": null, "subheading": "Subcortical Structures", "subheading_instructions": "", "type": "subheading" }, { "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Caudate (C)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "C", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }, { "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Internal Capsule (IC)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "IC", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }, { "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Lentiform nucleus (L)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "L", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }, { "inct": null, "option_fhir_rules": null, "subheading": "MCA Cortex", "subheading_instructions": "", "type": "subheading" }, { "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Insular Ribbon (I)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "I", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }, { "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Anterior MCA cortex (M1)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M1", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }, { "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "MCA cortex lateral to the insular ribbon (M2)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M2", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }, { "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "Posterior MCA cortex (M3)", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M3", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }, { "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "<p>Anterior cortex immediately rostral to M1 (M4)</p>", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M4", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }, { "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "<p>Lateral cortex immediately rostral to M3 (M5)</p>", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M5", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" }, { "conditionality": "", "default": 0, "label_en": "<p>Posterior cortex immediately rostral to M3 (M6)</p>", "md_calc_info_concept": null, "name": "M6", "option_fhir_rules": null, "optional": false, "options": [ { "label": "No", "value": 0 }, { "label": "Yes", "value": -1 } ], "show_points": true, "tips_en": "", "type": "toggle" } ]
instructions
To compute the ASPECTS, 1 point is subtracted from 10 for any evidence of early ischemic change for each of the defined regions.
published
2022-04-21T20:29:13.418Z
purpose
[ "Prognosis" ]
search_terms
[ "CT", "stroke", "ischemic", "prognosis" ]
seo
{ "keywords_en": "aspect score, aspect, early stroke, stroke, cva, id cva, id stroke early, stoke severity using CT, stroke severity CT, stroke prognosis", "meta_description_en": "The Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) determines Middle Cerebral Arterial (MCA) stroke severity using available computed tomography data." }
specialty
[ "Critical Care (Neurologic)", "Emergency Medicine", "Internal Medicine", "Neurology", "Neurosurgery", "Radiology" ]
departments
[ "Neurologic" ]
tags
[]
version_number
1
versions
[]
related
[ { "calcId": 1890, "short_title_en": "Modified Rankin Scale", "slug": "modified-rankin-scale-neurologic-disability" }, { "calcId": 10504, "short_title_en": "GARFIELD-AF", "slug": "garfield-af" }, { "calcId": 10480, "short_title_en": "TNKase Dosing", "slug": "tenecteplase-dosing" } ]
ismed
true
section
[ "whenToUseViewed", "pearlsPitfallsViewed", "whyUseViewed", "nextStepsViewed", "evidenceViewed" ]
cleaned_departments
[ "neurology" ]
cleaned_use
[ "Patients presenting in the first minutes and hours of a stroke with clinical suspicion for middle cerebral artery occlusion." ]
pub
false